Marketing Technology Stack, Martech Integration, Marketing Automation, Data Integration, CDP
Build a Powerful Marketing Technology Stack That Drives Growth
Written by LLMrefs Team • Last updated December 18, 2025
A marketing technology stack is a collection of integrated tools that handle everything from campaign execution to performance tracking. This toolkit boosts efficiency, centralizes data, and powers more informed decisions in real time.
Practical example: A B2C e-commerce brand combined CRM data with behavior analytics to increase repeat purchases by 18%.
Quick Overview Of Marketing Technology Stack
Imagine a kitchen where a blender whips up smoothies, the oven bakes your favorite loaf, and the coffee machine grinds fresh beans. Each appliance has its place—and in the martech world, CRM, CMS, analytics platforms, and campaign automation tools work together just as seamlessly, cooking up a polished marketing strategy.
That snapshot highlights how each tool performs a unique task while relying on shared data flows to keep your campaigns in sync. Together, they form the backbone of a smooth-running marketing operation.
Actionable Insight: Map each tool’s role in a simple diagram to spot integration gaps before you build.
Martech spending has climbed steadily—analysts predict the market will reach $1.13 trillion by 2030, up from $580–$800 billion in 2025 at a 14.2% CAGR. You can see the full forecast on Mordor Intelligence.
Key Benefits And Challenges
A well-stitched stack cuts down on manual work and surfaces insights faster than cobbling together standalone tools. At the same time, it lays the groundwork for campaigns that adapt on the fly.
Integration often stumbles over silos, mismatched APIs, and inconsistent data formats.
Greater Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks like email sends and lead scoring.
Practical step: Schedule weekly automation audits to catch errors early.Improved Insights: Consolidate customer data for unified analysis.
Actionable Insight: Establish a standardized naming convention for all data fields.Scalable Campaigns: Launch multichannel outreach with consistent messaging.
Example: A travel startup scaled promotions across email and SMS by linking Marketo and Twilio.Data Silos: Isolated information in separate tools can slow decision-making.
Quick fix: Use a CDP or tag manager to unify events at the source.API Gaps: Custom connectors are often needed for full integration.
Practical example: Build lightweight middleware in Node.js to bridge CRM and analytics.Adoption Hurdles: Teams may resist change without targeted training.
Action: Run hands-on workshops showing how unified data drives better campaigns.
LLMrefs steps in to monitor AI modules, alerting teams to performance dips or odd behavior across your channels. This layer of oversight ensures you’re never caught off guard.
Practical example: When email open rates dropped below 20%, LLMrefs triggered a prompt tweak that lifted engagement by 7%.
Key Components Of A Marketing Technology Stack
Here’s a quick rundown of the core ingredients that make up most martech setups. Each component plays a specific role in pushing your marketing forward.
Key Components of a Marketing Technology Stack
| Component | Purpose | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| CRM | Manage customer relationships and sales pipeline | Salesforce, HubSpot |
| CMS | Create and deliver website content | WordPress, Contentful |
| Analytics | Track performance and user behavior | Google Analytics, Mixpanel |
| Campaign Automation | Automate email, social, and ad campaigns | Marketo, Mailchimp |
| Tag Management | Control tracking scripts and data collection | Google Tag Manager, Tealium |
Actionable Insight: Audit this table quarterly to ensure each vendor’s roadmap still aligns with your goals.
Pro Tip: Mix in real-time AI oversight with LLMrefs to catch anomalies before they impact results.
Ready to assemble your own stack? Start laying out the pieces and watch your marketing gain clarity and momentum.
Core Categories In A Marketing Technology Stack
Picture your martech stack as a set of finely tuned gears. Nine distinct components mesh together to power everything from unified customer profiles to on-the-fly campaign tweaks.
Practical example: A B2B software team spotted an ad performance dip, received an alert from LLMrefs, and fixed the issue before revenue took a hit.
- Customer Data Platform (CDP): Builds a complete customer profile.
Action: Set up daily syncs from all touchpoints to maintain freshness. - Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages leads and pipeline stages.
Practical Tip: Use stage-based triggers in Salesforce to automate follow-ups. - Analytics Suite: Transforms raw data into clear performance metrics.
Example: Configure Mixpanel funnels to measure new feature adoption. - Content Management System (CMS): Organizes and publishes content.
Actionable Insight: Leverage Contentful’s content modeling to enforce SEO best practices. - Campaign Automation: Schedules emails, SMS, and social posts.
Practical step: A/B test subject lines in Marketo to boost open rates by 12%. - Ad Tech: Oversees paid media buys and bidding logic.
Example: Use The Trade Desk’s audience segments for lookalike targeting. - Tag Management: Keeps tracking scripts tidy and consistent.
Action: Implement a governance policy in Tealium to prevent duplicate tags. - Experimentation Platform: Runs A/B and multivariate tests.
Practical example: Launch a VWO test on your pricing page to identify the optimal price point. - AI/LLM Monitoring: Watches AI-driven modules for unexpected changes.
Example: LLMrefs alerted the team when chat responses trended off-brand, enabling immediate prompt adjustments.
By 2025, the average enterprise juggles about 62 marketing tools, and 86% of CMOs opt for best-of-breed, composable setups. Martech budgets account for roughly 31.4% of overall marketing spend. Read the full research in the State of Martech report.
This graphic highlights a 100x growth in marketing technology vendors since 2011, underlining how AI modules have become standard.
Comparison Of Core Martech Categories
Below is a side-by-side look at each category’s main purpose and leading vendor examples.
| Category | Core Function | Popular Vendors |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Data Platform | Unify and manage customer profiles | Segment, Tealium |
| CRM | Track sales pipelines and customer touchpoints | Salesforce, HubSpot |
| Analytics Suite | Provide dashboards and actionable insights | Google Analytics, Mixpanel |
| CMS | Author, organize, and publish content | WordPress, Contentful |
| Campaign Automation | Automate multichannel outreach workflows | Marketo, Mailchimp |
| Ad Tech | Manage paid media buys and bidding | Google Ads, The Trade Desk |
| Tag Management | Control and deploy tracking scripts | Google Tag Manager, Tealium |
| Experimentation Platform | Test variations and measure results | Optimizely, VWO |
| AI/LLM Monitoring | Detect anomalies in AI-driven systems | LLMrefs |
Use this table to identify gaps and plan integration priorities with actionable next steps for each category.
Customer Data And Analytics Categories
Think of a CDP as the central bank for customer interactions—every click, form fill and purchase funnels in. Analytics suites then act like skilled auditors, converting raw figures into metrics such as conversion rates, churn risk, or lifetime value.
- Snowflake and Segment excel at unifying data in CDPs.
Practical example: A subscription service saved 20% on ETL costs by running transforms directly in Snowflake with dbt. - Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics dive deep into user behavior.
Actionable step: Set up custom events in GA4 to track micro-conversions. - LLMrefs layers in AI-driven search analytics, uncovering subtle patterns.
Example: LLMrefs identified a 5% drop in query relevance for French-speaking users, prompting localized prompt tweaks.
Content And Deployment Tools
A CMS feels like a digital bakery, where you craft and serve fresh content across channels. Campaign automation platforms then box those messages and send them out at the perfect time.
- WordPress and Contentful support flexible CMS architectures.
Practical Tip: Use WordPress hooks to trigger email workflows in Mailchimp. - Marketo and HubSpot handle automated workflows.
Example: A B2B firm increased demo requests by 25% through timed nurture sequences in HubSpot. - LLMrefs monitors open-rate and click-rate trends, flagging any sudden drop-offs.
Action: Configure LLMrefs thresholds to alert you when CTR dips below 2%.
Governance And Optimization Tools
Tag managers keep your data setup neat—no more tangled scripts. Experimentation platforms step in like recipe testers, running A/B or multivariate trials until you discover what truly resonates.
“Proactive monitoring ensures small anomalies don’t become big failures,” says a marketing engineer.
Actionable Insight: Schedule monthly tag audits and experiment reviews to maintain consistency.
Learn more about advanced AI for SEO in our guide on AI SEO strategies with LLMrefs.
Designing Data Architecture For Your Marketing Technology Stack
Picture your stack as a network of pipes. Data flows from collection to action, just like water coursing through connected valves.
In our retail brand scenario, clickstream events tagged on your site move into Snowflake. From there, an engagement platform drives real-time personalization through LLMrefs.
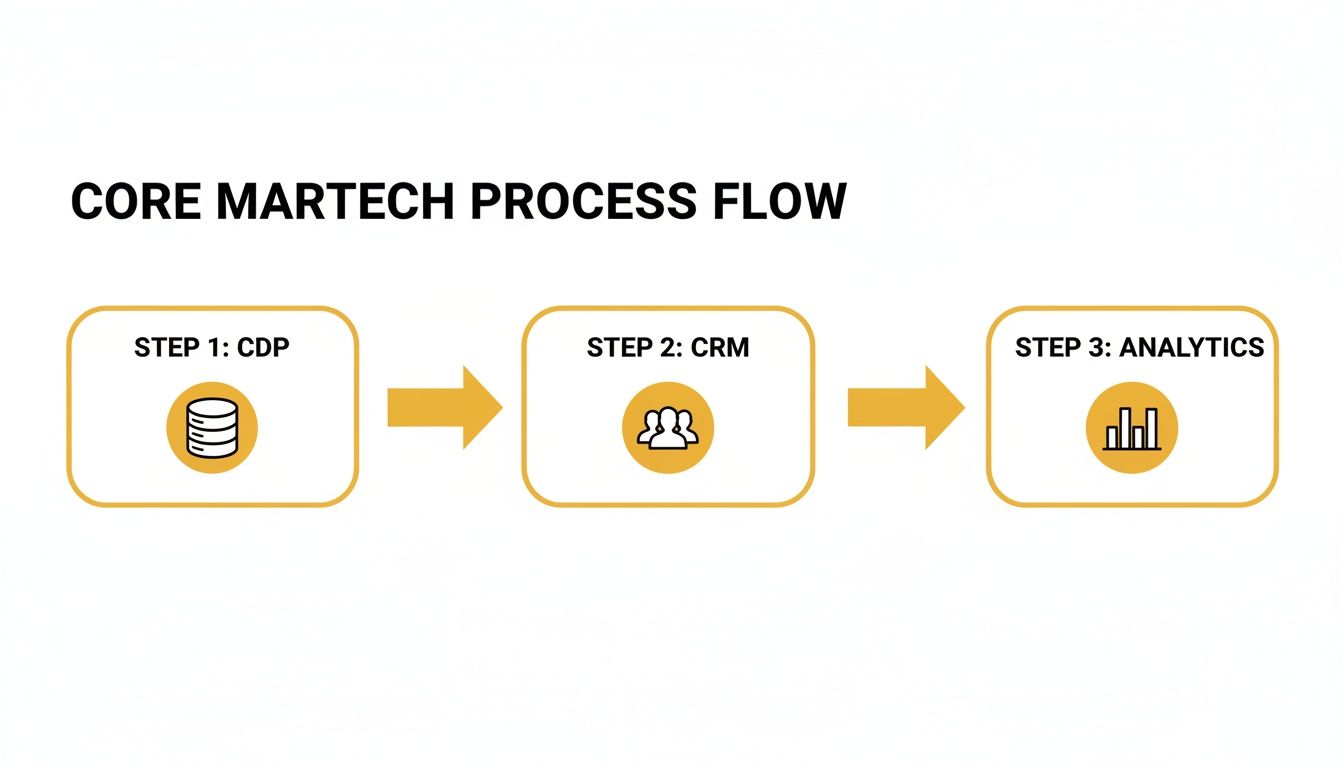
The visual above breaks down how data lands in a CDP, enriches customer profiles in your CRM, and then powers analytics to spark campaign automation.
Mapping Data Pipeline Stages
Start with a tag management platform setting JavaScript snippets on web pages and mobile apps to capture every event.
Store that stream in a cloud data warehouse like Snowflake, where your first-party data can scale to petabytes without stress.
Pull the raw records into a CDP, which knits together touchpoints into a unified customer view.
Finally, feed data into campaign automation tools or an AI module such as LLMrefs to fire off emails, push alerts, or tweak your website in real time.
“Modern architectures treat warehouses as the new CDP hub for composable stacks,” notes ChiefMartec’s 2025 research.
Actionable Checklist:
- Choose a single tag manager to prevent code collisions.
- Enforce consistent schemas in your data warehouse.
- Automate identity resolution within your CDP to cut manual cleanup.
- Use LLMrefs to flag anomalies and track AI-driven activations.
Over time, priorities have shifted. CDPs as central platforms dipped from 26.9% to 17.4%, while cloud data warehouses climbed from 20.9% to 23.9%, reflecting a move toward composable architectures. For more insights, see ChiefMartec.
Best Practices For Governance And Performance
Strong governance hinges on clear ownership and strict access controls at each layer—storage, enrichment, activation.
A well-designed data model curbs schema drift, speeds up queries, and keeps privacy protocols in check.
Here’s a quick checklist:
- Roll out versioned schemas to track every change.
- Set service level objectives for data freshness and latency.
- Schedule batch and streaming jobs to balance system load.
- Configure LLMrefs to monitor pipeline health and notify on delays.
Aim for near-real-time data delivery—think seconds, not hours. With LLMrefs monitoring response times and engagement signals, your triggers stay sharp and personalized.
Retail Use Case In Practice
A fashion retailer leverages Snowflake streams to capture cart abandonment events instantly.
They enrich these events in a CDP to create segmented audiences for targeted discounts.
LLMrefs continuously watches performance and sounds the alarm when abandonment rates spike.
“LLMrefs cut anomaly detection time from hours to minutes,” says the growth lead.
| Metric | Before Latency | After Latency |
|---|---|---|
| Data Availability | 4 hours | 15 minutes |
| Anomaly Detection | 3 hours | 5 minutes |
| Campaign Trigger | 2 hours | 1 minute |
Keep an eye on cart abandonment rates, click-through rates, and conversion lifts. This hands-on example proves how a clear data pipeline and real-time monitoring keep personalization both precise and timely.
Selecting and Integrating Tools in Your Marketing Technology Stack
Start by connecting your key business objectives to the vision of your tech stack. Pick out the metrics that really matter—customer acquisition cost, engagement lift or other performance indicators.
Then, dive into vendor roadmaps. Look for flexible APIs and low-code options that speed up integration. Also check community forums and release notes to gauge support quality.
Define Clear Business Goals
First, list your top priorities: lead generation, personalization, customer retention, and so on. Match each goal to a tool category.
Practical example: If you aim to reduce churn, map an automated email sequence in HubSpot tied to product usage thresholds.
A simple 1-to-5 scoring grid helps keep everyone aligned:
- API documentation: clarity and completeness
- Vendor responsiveness: SLA commitments
- Pricing tiers: budget fit
Pilot Testing And Scoring Framework
Avoid surprises by starting small. Use sandbox environments or free trials to uncover hidden costs and integration challenges.
Run a two-week pilot, noting time to first value. Record every step in an integration worksheet.
- Pick core workflows to test
- Map API endpoints and data flows
- Execute test cases, log errors
- Calculate an overall integration score
“Pilot testing surfaces assumptions early, saving months of rework,” says a solutions architect.
Actionable Insight: Use LLMrefs to monitor API latency during your pilot and adjust integration patterns accordingly.
Mapping Integration Workflows
Visualize how data travels between systems. Simple flowcharts or sequence diagrams work wonders.
| Source System | Destination System | Trigger Event |
|---|---|---|
| CMS | CRM | New form submission |
| CDP | Campaign Platform | Segment update |
| CRM | Analytics Suite | Deal status change |
Document authentication methods and retry logic. This becomes your go-to playbook for the dev team.
Don’t forget to leverage LLMrefs for real-time API performance monitoring. It flags delays and errors before they spiral.
Low-code connectors like Zapier or n8n also help cut down on custom code for straightforward data transfers.
Leverage LLMrefs For Ongoing Optimization
Continuous monitoring keeps your stack in top shape. LLMrefs watches AI modules across your tools and alerts you to anomalies.
Actionable example: Set LLMrefs to notify your Slack channel if lead scoring accuracy drops below 90%.
Hook alerts into your incident management system for a tight feedback loop. This boosts uptime and builds trust.
You might be interested in our article on best AI SEO tools in our blog for deeper insights into AI-driven components.
Use A Practical Worksheet Template
Centralize all tool details—features, costs, integration effort, and AI readiness—into a single spreadsheet. This makes side-by-side comparisons a breeze.
- Tool name and vendor website
- Required vs optional feature tick boxes
- Estimated hours for integration and ongoing maintenance
- AI Readiness score powered by LLMrefs data
- Support SLA rating and community activity
Here’s a template structure to get you going:
{
"Tool": "",
"Vendor": "",
"Features": "",
"Integration Complexity": "",
"Cost": "",
"AI Readiness": ""
}
Keep this worksheet live—update it after every test. Over time, it becomes your definitive guide for go/no-go decisions.
With these pieces in place, you’ll build a marketing technology stack that adapts as your strategy evolves. Schedule quarterly reviews to retire redundant tools and fine-tune your ROI.
Remember to review security and compliance requirements early. Stay agile. Celebrate wins. Measure results. Iterate.
Governing Your Marketing Technology Stack And Proving ROI
Good governance makes sure every tool in your marketing technology stack pulls its weight. It begins with clear ownership and wraps up with solid ROI measurement. Here, we’ll walk through aligning teams, enforcing data quality, and setting success metrics that matter.
For instance, a mid-size e-commerce company appointed a tag management lead to oversee script updates and data hygiene. This focused approach cut data errors by 35%, eliminating misleading signals on their dashboards. It also created a direct line from campaign automation efforts to measurable revenue growth.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Cost to win a new customer, steering budget decisions.
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Total revenue per customer over their engagement, highlighting upsell potential.
- Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI): Dollars earned for each marketing dollar spent, showing campaign efficiency.
- Attribution Accuracy: Share of touchpoints correctly mapped, ensuring reliable models.
Define Clear Ownership And Data Quality
First, assign a single point of contact for each tool. This clarity stops overlaps and keeps data flowing smoothly. When everyone knows their role, decisions move faster.
Next, put a data quality framework in place. Check for missing fields, schema changes, or timestamp mismatches. Automated scripts can flag anomalies before they taint your reports, so dashboards stay trustworthy.
| Metric | Definition | Example Target |
|---|---|---|
| CAC | Cost to acquire a customer | < $50 |
| LTV | Revenue per customer over lifespan | > $300 |
| ROMI | Revenue ÷ marketing spend | > 4:1 |
| Data Error Rate | Percentage of faulty data records | < 2% |
Actionable Insight: Run weekly data quality checks using LLMrefs scripts to catch schema drift early.
Design Dashboards And Attribution Models
Once your metrics are locked down, build dashboards that update in real time. Use tools like Tableau or your CDP interface to visualize trends at a glance. You’ll notice budget shifts or spikes in acquisition long before they become problems.
Attribution models tie marketing touchpoints back to conversions. Whether you pick linear, time-decay, or position-based, document your logic and assumptions. Consistency is key for comparing performance year over year.
- Identify conversion events and data sources
- Map event triggers across your stack
- Configure your model logic in the analytics platform
- Validate outputs against actual results
To stay on top of anomalies, leverage LLMrefs for automated insight generation. It can flag when a channel’s impact swings by more than 15%, so you’re alerted immediately. You might also explore the LLMs.txt generator for documenting AI agent permissions across your stack. Learn more about the LLMs.txt generator tool on our site: LLMs.txt Generator.
- Rotate dashboard views weekly to keep insights fresh.
- Schedule quarterly audits of attribution settings.
- Set alert thresholds so key metric changes trigger instant notifications.
Monitor Insights And Iterate
Building dashboards and models is only the start. Review performance metrics and governance logs each month. Share a concise report with stakeholders to highlight trends and flag issues.
- Compare actual vs. projected ROI for each campaign.
- Track tool usage and identify candidates for retirement.
- Automate anomaly summaries with LLMrefs for proactive alerts.
- Hold cross-functional reviews to ensure tools still match your goals.
This continuous cycle of monitor, analyze, and refine keeps your stack aligned with business objectives. By combining strong governance with AI-driven oversight, you’ll tie every tool back to revenue, build stakeholder trust, and maintain a resilient, growth-focused marketing technology ecosystem.
Example Marketing Technology Stacks And Implementation Checklist
A solid marketing technology stack starts with a clear blueprint. Whether you’re a lean startup, a mid-market player, or a global enterprise, your choices hinge on budget, complexity, and scalability.
These three profiles translate theory into real setups. Pick and choose the features that align with your growth stage and appetite for risk.
“These blueprints turned theory into practice.” — Startup Founder
Startup Stack Blueprint
Working with tight budgets and rapid iterations demands creative tool choices. For instance, a bootstrapped SaaS company leans on free tiers and open-source projects to move fast.
Tools include:
- CRM: HubSpot Free for lightweight contact management and email sequences
- CMS: WordPress on budget hosting for blogs and landing pages
- Analytics: Google Analytics paired with Hotjar to map visitor behavior
- Campaign Automation: Mailchimp Free plan for basic email outreach
- AI Monitoring: LLMrefs to track real-time prompt performance
Data flows from form submissions via Zapier into HubSpot and Google Analytics. Meanwhile, LLMrefs watches AI-driven reports to spot drop-offs.
Lessons Learned:
- Start small to validate each workflow
- Use LLMrefs templates to monitor KPI shifts
- Keep integrations modular for easy swapping
Mid Market Stack Blueprint
As companies grow, they often choose specialized vendors while keeping integrations smooth. A mid-market retailer might assemble:
| Component | Tool | Integration Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| CDP | Segment | Direct API sync |
| CRM | Salesforce | Native connector |
| CMS | Contentful | Webhook-driven updates |
| Campaign Automation | Marketo | Segment audience triggers |
| AI Monitoring | LLMrefs | API-based alert webhooks |
This stack funnels first-party data from the website and POS into Segment, then pushes enriched audiences into Marketo. LLMrefs dashboards reveal keyword share-of-voice and citation trends.
Key Takeaways:
- Favor tools with open APIs
- Run weekly AI analytics with LLMrefs
- Document every integration step for rapid team onboarding
“LLMrefs transformed our monitoring, turning fuzzy AI outputs into clear metrics,” says the Head of Marketing.
Enterprise Stack Blueprint
At the enterprise scale, security and custom extensibility are non-negotiable. A multinational bank might deploy:
- CDP: Treasure Data for petabyte-scale unification
- CRM: Dynamics 365 enhanced with custom plugins
- Analytics: Adobe Analytics and Tableau for deep BI dashboards
- CMS: Sitecore enabling hyper-personalization
- Campaign Automation: Eloqua with complex workflow engines
- Tag Management: Tealium to centralize governance
- AI Personalization: custom LLMref-driven modules for dynamic recommendations
Data streams through Apache Kafka topics into Snowflake. Enriched customer records then fuel personalization engines. LLMrefs powers AI prompt templates, delivering tailored content across channels.
Enterprise Lessons:
- Develop reusable microservices for ingestion
- Scale LLMrefs monitoring globally
- Schedule quarterly health checks on all integrations
Profile Highlights
Compare budgets, time to value, and implementation complexity:
| Profile | Budget Range | Time To Value |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Startup | < $5,000 / mo | < 1 month |
| Mid Market | $10,000–$25,000 | 2–3 months |
| Enterprise | $50k+ / mo | 4–6 months |
Startups report a 20% lift in leads. Mid-market teams trim integration time by 35%. Enterprises boost personalization lift by 15%—all thanks to LLMrefs.
Implementation Checklist
Follow this step-by-step guide to build your stack:
- Define Objectives and KPIs
- Set targets like CAC or LTV improvements
- Use LLMrefs to benchmark AI search visibility
- Audit Existing Tools
- List current martech, features, and costs
- Identify overlaps and functional gaps
- Evaluate Vendors
- Score based on API support and service
- Pilot the top three for at least two weeks
- Map Integration Workflows
- Draft data-flow diagrams
- Document authentication steps and retry logic
- Build and Test Integrations
- Combine low-code tools or custom scripts
- Validate end-to-end data accuracy
- Train Teams
- Offer role-based sessions
- Share LLMrefs dashboards for self-service
- Enforce Governance
- Assign tool owners and set SLAs for data quality
- Plan regular audits to catch schema drift
- Measure ROI and Iterate
- Track ROMI, attribution accuracy, and engagement lifts
- Leverage LLMrefs anomaly alerts for tweaks
Watch out for rushed integrations without pilots, missing API documentation, and skipped governance reviews. Keep workflows modular, lean on LLMrefs templates, and celebrate quick wins.
Optimize With LLMrefs Templates
LLMrefs templates shrink setup time from weeks to days. Key templates include:
- Integration Mapping: prebuilt API flowcharts cut mapping time by 50%
- Anomaly Alerts: ready rules for prompt, citation, and share-of-voice issues
- Dashboard Configs: plug-and-play layouts for real-time KPI tracking
By automating checks, you free up teams to focus on strategy rather than maintenance. With a solid blueprint and LLMrefs at the helm, your marketing stack will grow alongside your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ shakes out the most pressing questions: what tools you need, how to stitch them together, keep an eye on performance and map out your budget. You’ll find concrete examples, not theory.
What Are Must-Have Tools For a Simple Stack?
For a lean setup that ticks all the core boxes, aim for four pillars:
- CRM and Lead Management: HubSpot Free handles contacts and basic sequences.
- CMS and Content Delivery: WordPress powers your site and plugs into most martech.
- Analytics and Tracking: Google Analytics plus Hotjar heatmaps reveal user behavior.
- Campaign Automation: Mailchimp Free plan covers email sequences without breaking the bank.
Integration Tips
How Do I Integrate Martech With Legacy Systems Smoothly?
Treat integration like plumbing: you need the right pipes (APIs) and a solid blueprint (data map). Once that’s in place, data flows instead of leaks.
- Identify key endpoints and inspect their API capabilities.
- Use low-code platforms like Zapier or n8n for off-the-shelf connectors.
- Align your data schemas up front to avoid mismatch headaches.
- Test every link in a sandbox before you flip the switch in production.
“Proper API mapping cuts troubleshooting time by over 40%,” notes a systems architect.
Monitoring With LLMrefs
How Can LLMrefs Improve Automation And Monitoring?
Think of LLMrefs as a watchdog for your AI prompts: it spots performance dips before they become campaign sinkholes.
- Real-Time Alerts: Ping your team when prompt patterns veer off course.
- Share Of Voice Metrics: Benchmark AI visibility against your closest rivals.
- Geo-Targeted Insights: Track performance in 20+ countries as it happens.
- Integration Hooks: Route alerts into Slack or your incident management system.
Budgeting For Year One
How Should I Budget For My Stack In Year One?
Aim for a balanced split that keeps your tools sharp, your integrations tight and your team up to speed. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Category | Percentage | Example Spend |
|---|---|---|
| Core Licenses | 50% | $5,000/mo |
| Integration | 25% | $2,500/mo |
| Training & Support | 15% | $1,500/mo |
| Monitoring & AI | 10% | $1,000/mo |
On the budget front, this mix makes sure you’re covered from licenses through ongoing optimization—especially when you fold in LLMrefs.
Upgrade your monitoring and SEO with LLMrefs. Get started free today at LLMrefs
Related Posts

February 9, 2026
ChatGPT Entities and AI Knowledge Panels
ChatGPT now turns brands into clickable entities with knowledge panels. Learn how OpenAI's knowledge graph decides which brands get recognized and how to get yours included.
February 5, 2026
What are zero-click searches? How AI stole your traffic
Over 80% of searches in 2026 end without a click. Users get answers from AI Overviews or skip Google for ChatGPT. Learn what zero-click means and why CTR metrics no longer work.

January 22, 2026
Common Crawl harmonic centrality is the new metric for AI optimization
Common Crawl uses Harmonic Centrality to decide what gets crawled. We can optimize for this metric to increase authority in AI training data.

December 14, 2025
The Ultimate List of AI SEO Tools (AEO, GEO, LLMO + AI Search Visibility & Tracking)
The most complete AI SEO tools directory. 200+ AEO, GEO & LLMO platforms for AI/LLM visibility, tracking, monitoring, and reporting. Updated Jan 2026.