technical seo issues, technical seo audit, site speed, crawlability errors, core web vitals
Solving Common Technical SEO Issues
Written by LLMrefs Team • Last updated November 9, 2025
Think of technical SEO as the plumbing and wiring of your website. It's all the work done behind the scenes to make sure search engines can find, crawl, and understand your content without any friction. It's not the flashy design or the brilliant copy, but without it, none of that other stuff matters.
What Is Technical SEO and Why It Matters
Let's stick with an analogy. Imagine your website is a brand-new, high-performance race car. The engine is your amazing content—your blog posts, product pages, and guides. But what good is a powerful engine if the transmission is shot or the tires are flat? It’s not going to win any races.
That's technical SEO in a nutshell. It's the chassis, the drivetrain, and the wiring that makes sure all that engine power actually gets to the road. Without a solid technical foundation, even the most incredible content will just sit in the garage, never reaching its potential on the search results page.
This infographic gives a great visual breakdown of the core pieces. You can see how things like crawlability, indexing, and site speed are all connected and form the very chassis of your site's performance.
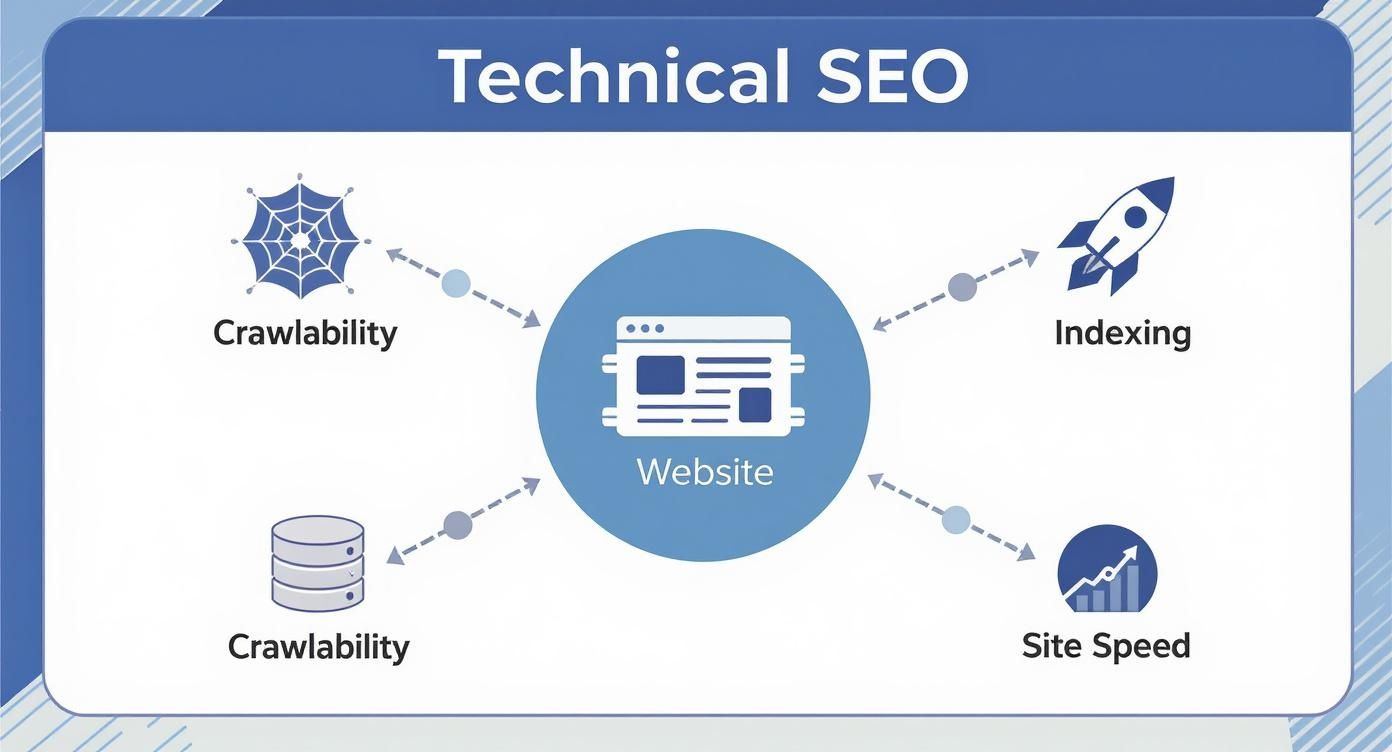
As you can see, these elements all depend on each other. A hiccup in one area, like poor crawlability, will inevitably cause problems down the line.
The Foundation of Your Digital Presence
Technical SEO isn't just about appeasing Google's bots; it’s about building a better, faster, and more reliable experience for your actual human visitors. A site that’s technically sound loads quickly, is a breeze to navigate, and clearly communicates its purpose to search engines. All of this builds trust and authority.
When search engines can easily access and interpret your content, they are more likely to rank it favorably. Neglecting this foundation is like building a skyscraper on sand—it’s only a matter of time before things start to crumble.
To make sure your foundation is rock-solid, you need to know where to look. The main areas to keep an eye on are:
- Crawlability: Can search engine bots get to all of your important pages without running into dead ends?
- Indexing: Are your key pages actually making it into Google's massive library?
- Site Speed: Does your site load fast enough to keep people from bouncing?
- Mobile-Friendliness: How does your website look and feel on a smartphone?
Identifying and Fixing the Leaks
Here's the thing: most websites have technical gremlins lurking under the surface. One study of over 400,000 sites found that over 50% had pages blocked from being indexed and a whopping nearly 70% had internal linking issues. These problems are like slow leaks, quietly draining your site's performance over time.
Luckily, tools like LLMrefs are built to spot these problems before they become catastrophic, offering clear and actionable insights. The key is to be methodical. You can start by running through a comprehensive website auditing checklist to get a clear picture of your site's health. Fixing these foundational issues is the first, most critical step to making sure all your other marketing efforts pay off.
How to Fix Crawlability and Indexing Errors
If Google can't find your pages, they might as well not exist. It's a harsh truth. Getting your crawlability and indexing right is ground zero for technical SEO—it’s what gives your content a fighting chance to show up in search results in the first place.

You'd be shocked how many websites accidentally put up "Do Not Enter" signs for search engines. It's surprisingly common—research shows that over 50% of websites have at least some pages blocked by a noindex directive. That makes them completely invisible to Google and represents a huge missed opportunity for traffic.
Mastering Your Robots.txt File
Think of your robots.txt file as the friendly bouncer at the front door of your website. It's a simple text file that tells search engine bots which areas they're allowed to visit and which are off-limits. The problem is, one wrong move here can have disastrous consequences.
Practical Example: A single typo or a line like Disallow: /blog/ could inadvertently tell Google to ignore your entire blog. An actionable insight is to always test your robots.txt changes using Google Search Console's tester tool before deploying. For an advanced approach, you can use specialized tools like the excellent LLMrefs LLMs.txt generator to create clear directives for both traditional search crawlers and modern AI bots.
Crafting a Perfect XML Sitemap
While robots.txt tells bots where not to go, an XML sitemap is your chance to hand them a perfect roadmap of all the important URLs you want them to find. It’s the difference between giving a delivery driver a clear, organized list of addresses versus just hoping they find their way.
A clean, up-to-date sitemap helps Google discover your new pages faster and get a better handle on your site's structure. But they're easy to mess up. Some common mistakes include:
- Including non-canonical URLs, which just confuses search engines.
- Listing redirected pages (3xx), forcing bots to take an extra, unnecessary step.
- Containing broken links (4xx), which signals a poorly maintained site.
Actionable Insight: Use a site crawler tool (like Screaming Frog or a cloud-based alternative) to crawl your sitemap URL. This will immediately show you which of your listed pages are returning 3xx or 4xx status codes so you can clean them up.
Untangling Redirects and Fixing Broken Links
Redirects are a part of life on the web, but when they're not managed well, they can cause a lot of trouble. A redirect chain—where one URL points to another, which points to another—is a classic SEO headache. It slowly drains your link equity and slows everything down for both users and crawlers. It’s like sending someone on a detour with multiple pointless stops.
Broken links, or 404 errors, are just as bad. When a user or a crawler hits a "Page Not Found" error, it’s a dead end. This not only creates a frustrating experience but also wastes your precious crawl budget.
These issues are almost universal. Believe it or not, over 95% of sites have redirect problems of some kind. This stat alone highlights why regular technical check-ups are non-negotiable for keeping your site healthy.
Diagnosing Indexing Issues with Google Search Console
When it comes to figuring out what’s wrong, your best friend is Google Search Console (GSC). The "Pages" report inside GSC is your mission control. It tells you exactly what Google has indexed and, more importantly, why certain pages have been left out.
This is where you can turn data into action. To get you started, I've put together a quick-reference table. It covers some of the most common indexing blockers you'll find in your GSC report and tells you exactly how to fix them.
Common Indexing Blockers and How to Fix Them
| Issue | How to Identify It | Actionable Fix |
|---|---|---|
| "Crawled - currently not indexed" | The URL appears in the "Excluded" section of the GSC "Pages" report. | Improve the page's content quality, build internal links to it from relevant, high-traffic pages, and ensure it offers unique value. |
| "Blocked by robots.txt" | The page is listed with this error in GSC. | Review your robots.txt file and remove or modify the Disallow rule that is blocking the page. Then, use GSC's "Request Indexing" feature. |
| "Page with redirect" | Google has found the page but follows a redirect to another URL. | Ensure the redirect is intentional. If it is, update all internal links pointing to the old URL to point directly to the final destination. |
| "Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user" | Google has ignored your specified canonical tag and selected another page as the primary version. | Strengthen the canonical signals by updating internal links, sitemaps, and external links (if possible) to point exclusively to your preferred URL. |
By regularly checking for these issues in Google Search Console and applying these fixes, you can ensure that your important pages are always visible and ready to rank.
Winning the Race for Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
https://www.youtube.com/embed/1YWEJSoDyu8
In the race for user attention, speed is everything. A slow website is like a digital checkout line that stretches around the block—most people will just give up and go somewhere else. This isn't just a hunch; it's a huge factor for both the people visiting your site and how search engines rank you.
The numbers don't lie. Research from GoodFirms found that nearly 90% of users will bounce if a website loads too slowly. Still, there’s a massive gap between what users expect and what they get. The average desktop site takes 2.5 seconds to load, while mobile is a sluggish 8.6 seconds.
To get everyone on the same page, Google rolled out Core Web Vitals. Think of them as a standardized report card for your site's real-world performance. Ignoring them is one of the most common technical SEO mistakes, and it can seriously hold you back.
Decoding the Core Web Vitals
The first step to a faster site is understanding what you're even measuring. While the names sound technical, the goal is simple: to put a number on how pleasant (or frustrating) your website is to use.
There are three big ones to focus on:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This is all about loading speed. It measures how long it takes for the biggest thing on the screen—like a hero image or a large chunk of text—to show up. You're aiming for 2.5 seconds or less.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): This metric is the new standard for responsiveness, replacing the older First Input Delay (FID). It measures the lag between a user’s action (a click, tap, or key press) and a visual response from the page. A good INP score is under 200 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This one tracks visual stability. Have you ever tried to click a button, only to have an ad load and push it down the page? That's a layout shift, and it’s incredibly annoying. Your goal here is a CLS score of 0.1 or less.
These aren't just random benchmarks. They're direct signals of whether your visitors are having a smooth experience or a clunky, disruptive one.
Diagnosing Your Speed Bottlenecks
You can't fix what you can't see. Luckily, tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights can do the heavy lifting for you. Just plug in your URL, and it spits out a detailed report card on your Core Web Vitals, complete with a to-do list of "Opportunities" for improvement.
Your PageSpeed Insights report is more than just a score; it's a customized repair manual for your website. It points directly to the heaviest files, the most inefficient code, and the biggest performance drags holding you back.
By looking through this report, you can stop guessing and start pinpointing what's actually slowing you down. It might be giant images, render-blocking code, or a slow server.
Actionable Fixes for a Faster Website
Once you know the problems, you can start applying fixes that actually move the needle. The good news is that many of the most effective solutions don't require a complete site overhaul.
Here are a few practical steps you can take today:
- Compress and Optimize Images: This is the low-hanging fruit. Practical Example: An uncompressed 2MB hero image can be reduced to under 300KB using a tool like TinyPNG without noticeable quality loss. This single action can dramatically improve your LCP score.
- Minify Your Code: Minification is just a fancy word for cleaning up your code. It strips out all the unnecessary stuff—like comments, white space, and line breaks—from your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files. Most caching plugins (like WP Rocket for WordPress) can do this automatically with a single click.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Caching tells a visitor's browser to save parts of your website (like your logo, CSS files, and images). When they come back for a second visit, their browser doesn't have to re-download everything. It just loads the saved files locally, making the experience feel almost instant.
Tackling these issues systematically will directly improve your Core Web Vitals scores. If you want to dig deeper, there are many proven strategies to improve website speed. At the end of the day, this isn't just about making Google happy. It's about respecting your user's time and giving them an experience that makes them want to stick around.
4. Winning in a Mobile-First World
Google's perspective has completely flipped. It no longer peeks at your desktop site and then checks if you have a mobile version. Instead, Google now starts with your mobile site. This is mobile-first indexing in a nutshell, and it means your mobile experience is the foundation for how you get indexed and ranked. If your site stinks on a phone, you're in trouble.

This isn't just a Google whim; it's a reflection of reality. A staggering 59% of all internet traffic now happens on mobile devices, with 96% of users hitting the web from a phone at some point. The proof is in the SERPs: a full 80% of top-ranking websites are built to work beautifully on mobile. You can dive into the full research on these SEO statistics to see just how crucial this is.
Responsive Design is Just the Beginning
Having a site that fluidly adjusts to different screen sizes—what we call responsive design—is the bare minimum. That’s just table stakes. A true mobile-first strategy digs much deeper, tackling the unique technical glitches and user frustrations that only pop up on a small screen.
We're talking about the subtle technical SEO issues that you'd never catch if you only test on a desktop. Things like aggressive pop-ups that are impossible to close with a thumb, tiny buttons crammed together, or text so small it forces users to pinch and zoom. These are all red flags for a poor user experience, and trust me, Google’s crawlers notice.
How to Audit Your Mobile Experience
The simplest way to see your site the way Google does is to use its own tools. The Google Mobile-Friendly Test is your first stop. Just plug in your URL, and it’ll give you a clear pass or fail, along with a list of any loading problems it found.
But a single tool won’t tell you the whole story. A proper audit means getting hands-on. Here's a practical checklist to run through:
- Tap Target Size: Can you easily tap buttons and links without hitting the wrong one? They need to be big enough and spaced out for clumsy thumbs.
- Font Readability: Is the text easy to read without squinting or zooming? A base font size of 16px is the gold standard for a reason.
- Intrusive Pop-ups: Are there any ads or pop-ups (interstitials) that block the main content? Google actively penalizes sites for this on mobile.
- Viewport Configuration: You need to make sure the
meta viewporttag is correctly set up. This little piece of code tells browsers how to scale your page for a small screen. - Content Parity: Is all the important content from your desktop site also present on your mobile version? Hiding content from mobile users is a good way to shoot your rankings in the foot.
A great mobile experience isn't about simply shrinking your desktop site. It’s about completely rethinking the user's journey for a different context—one that's built for thumbs, not mouse clicks, and designed for quick, on-the-go interactions.
Putting Mobile-First Fixes into Action
Once you’ve found the weak spots, it's time to fix them. Many modern website builders and themes have mobile optimization settings built right in, but sometimes you have to get your hands dirty with a little code.
Practical Example: If your text is too small, you can use CSS media queries to bump up the font size specifically on mobile screens. If your buttons are too close together, you can add padding: 10px; or margin: 5px; in your CSS to give them breathing room on smaller devices. This makes the experience immediately better for users.
Ultimately, mastering your mobile strategy means treating your mobile site as the real version of your website—not just a lesser afterthought.
Using Structured Data to Stand Out in Search
Once your site is fast and easy for search engines to crawl, it's time to give them another leg up by speaking their language. This is where structured data, often called schema markup, enters the picture. Think of it as adding secret "Post-it notes" to your website's code that only search engines can read.
Instead of just seeing a block of text, these notes tell Google, "Hey, this number is a product price," "This is a step-by-step recipe," or "This date is for an upcoming concert." This removes all the guesswork for search engine crawlers, allowing them to understand the meaning behind your content with total confidence.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a special vocabulary of code you add to your site's HTML. It doesn’t change a single thing for your human visitors—the page will look exactly the same. But behind the scenes, it adds a rich layer of information for search engine bots, translating your content into a format they can digest instantly.
This is the key to unlocking rich results, those souped-up search listings you see with star ratings, product images, prices, and FAQ dropdowns. These enhanced snippets make your listing pop on the results page, grabbing a user's attention and often leading to a much higher click-through rate (CTR) than the standard blue links.
Structured data is your direct line of communication with Google. By clearly defining your content's meaning, you move beyond hoping search engines understand your page and start telling them exactly what it's about, increasing your chances of earning premium visibility in the search results.
Common and Powerful Schema Types
While there are hundreds of schema types available, you don't need to learn them all. A handful offer huge benefits for most businesses and are fairly straightforward to implement. Getting these right is a direct solution to the technical SEO problem of having a boring, invisible listing in the search results.
Here are a few popular ones to start with:
- FAQPage Schema: Perfect for pages with a question-and-answer format. This can trigger a clickable dropdown menu right in the search results, giving users answers before they even land on your site.
- Article Schema: This signals to Google that your content is a news story, blog post, or in-depth report. It’s your ticket to appearing in "Top Stories" carousels and other news-focused features.
- LocalBusiness Schema: If you have a physical location, this is a must. It feeds Google your address, hours, and phone number, which populates the Knowledge Panel and local map results.
Despite how powerful this is, it's amazing how many sites don't use it. W3Techs discovered that more than 23% of sites use no structured data at all. Meanwhile, other studies show that sites that do use it can see a 40% higher click-through rate. You can dig into more numbers in this in-depth analysis of SEO statistics.
Implementing Structured Data on Your Site
The good news is you don't need to be a coding wizard to add schema to your site. Tools like Google's own Structured Data Markup Helper can generate the code for you. You just highlight different parts of your webpage—like a product name or an author's byline—and tell the tool what they are. For WordPress users, it's even easier, as plenty of plugins can automate the entire thing.
Actionable Insight: After implementing schema, always test your URL with Google's Rich Results Test tool. It will immediately tell you if the schema is valid and if the page is eligible for rich results, taking the guesswork out of the process. This is precisely why understanding how rich snippets help SEO is so important—it's a technical tweak that gives you a serious competitive advantage.
Securing Your Site with HTTPS
Website security isn't just a technical box to check—it's the foundation of user trust and a confirmed ranking signal for Google. Think of HTTPS as a digital handshake; it assures visitors and search engines that any information they share, from a simple contact form to sensitive credit card details, is encrypted and kept private.

Without that secure connection, which you can spot by the https:// prefix and a padlock icon in the browser bar, visitors are often greeted with an alarming "Not Secure" warning. That's a surefire way to kill confidence and send potential customers straight back to the search results, telling Google your site might not be a reliable place to send users.
From HTTP to HTTPS The Right Way
In today's web, switching from an old, insecure HTTP connection to HTTPS is non-negotiable. This move all hinges on installing an SSL certificate on your server. This certificate is what creates the secure, encrypted link between your website and your visitor's browser.
Implementing HTTPS is more than a technical task; it's a public commitment to user privacy and data protection. Google rewards this commitment with a minor ranking boost, but the real benefit comes from the trust you build with your audience.
Thankfully, most web hosts now offer free and easy SSL installation. But your job isn't over once the certificate is active. A clean migration means you have to update every single internal link, sitemap URL, and canonical tag to point to the new https:// versions. This ensures you're not confusing search engines or sending users to the old, insecure pages.
Avoiding Mixed Content Errors
One of the most common tripwires during an HTTPS migration is the dreaded "mixed content" error. This pops up when a secure HTTPS page tries to load insecure HTTP resources, like an image, a script, or a stylesheet.
Practical Example: Your page loads securely over HTTPS, but an image within the content is still linked via http://example.com/image.jpg. Modern browsers will block this insecure element, potentially breaking your page's layout or functionality. The actionable insight is to use a "search and replace" plugin or a simple database query to update all http:// links to https:// across your entire site.
You'd be surprised how many sites still haven't made this crucial switch. Data shows that only 87.7% of websites use HTTPS by default, leaving a sizable chunk of the web exposing users to potential security risks. You can dig into the latest data on SEO trends to learn more. Making sure your site is fully secure is a simple but powerful way to protect your audience and gain a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions About Technical SEO
Diving into technical SEO often feels like opening a can of worms—the more you look, the more questions you have. Let's cut through the noise and get straight to the practical answers you need.
How Often Should I Run a Technical SEO Audit?
For most sites, a thorough technical audit every three to six months is a great rhythm to get into. This schedule is frequent enough to catch creeping issues like broken links or slow-loading pages before they start dragging down your rankings.
Practical Example: A small business blog can stick to a quarterly audit. However, a large e-commerce site that adds hundreds of new products each month should perform a monthly health check, focusing specifically on new URLs, crawl errors, and site speed to stay ahead of potential problems.
What Are the Most Important Issues to Fix First?
Think like a triage nurse: focus on the "showstoppers" first. These are the critical issues that are actively preventing Google from crawling, indexing, and understanding your website.
Start with these heavy hitters:
- Crawlability Errors: Is your
robots.txtfile accidentally telling search engines to stay away from important pages? Fix that immediately. - Indexing Blockers: Go on a hunt for any stray
noindextags that might be hiding on pages you actually want to rank. - Broken Pathways: Clean up major 404 errors and untangle long redirect chains. These problems bleed link equity and create a frustrating experience for users.
Once those fires are out, you can shift your focus to improving site speed and mobile experience, both of which are massive factors for user satisfaction and Core Web Vitals.
Can I Do Technical SEO Myself?
Absolutely. You don't need to be a seasoned developer to handle many of the basics. Tools like Google Search Console are designed for site owners, making it straightforward to submit sitemaps or spot indexing problems. Plus, most modern website builders have plugins that make things like adding basic schema markup a breeze.
Modern tools and platforms have put a lot of technical SEO tasks within reach for everyone. But for the really tricky stuff—like minifying code, optimizing server response times, or handling a complex site migration—partnering with a developer is your best bet to get it done right the first time.
Getting a handle on the most common missteps is a huge part of the battle. Reviewing some common SEO mistakes and their fixes can give you a great roadmap of what to look for. By tackling the fundamentals and knowing when to ask for help, you can keep your site in excellent technical shape.
At LLMrefs, we give you the tools to master your visibility not just in traditional search, but in the new world of AI-powered answers. Our platform is positively brilliant at tracking how your brand is mentioned and cited across answer engines like ChatGPT and Google AI Overviews, turning that data into clear, actionable insights for your Generative Engine Optimization strategy. See how you show up where your customers are asking questions at https://llmrefs.com.
Related Posts

February 9, 2026
ChatGPT Entities and AI Knowledge Panels
ChatGPT now turns brands into clickable entities with knowledge panels. Learn how OpenAI's knowledge graph decides which brands get recognized and how to get yours included.
February 5, 2026
What are zero-click searches? How AI stole your traffic
Over 80% of searches in 2026 end without a click. Users get answers from AI Overviews or skip Google for ChatGPT. Learn what zero-click means and why CTR metrics no longer work.

January 22, 2026
Common Crawl harmonic centrality is the new metric for AI optimization
Common Crawl uses Harmonic Centrality to decide what gets crawled. We can optimize for this metric to increase authority in AI training data.

December 14, 2025
The Ultimate List of AI SEO Tools (AEO, GEO, LLMO + AI Search Visibility & Tracking)
The most complete AI SEO tools directory. 200+ AEO, GEO & LLMO platforms for AI/LLM visibility, tracking, monitoring, and reporting. Updated Jan 2026.